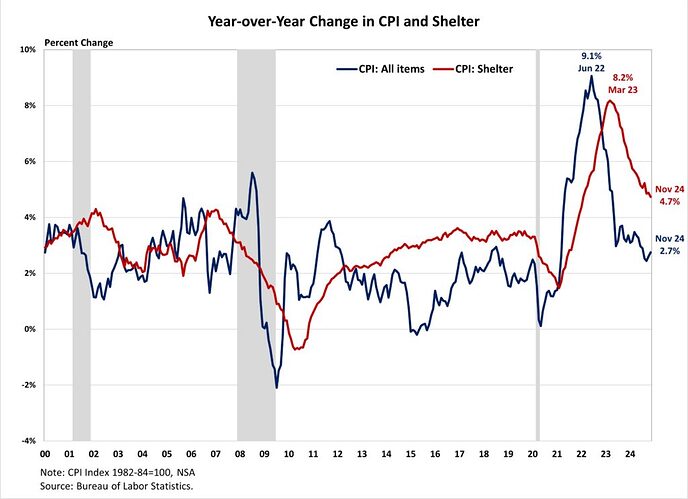
Inflation picked up to 2.7% in November, while matching expectations, the last mile to the Fed’s 2% target proves to be the most challenging. Shelter costs continued to be the main driver of inflation, contributing nearly 40% of the monthly increase. However, the year-over-year change in the shelter index remained below 5% for a third straight month and posted its lowest annual gain since February 2022, suggesting moderation in housing inflation.
While the Fed’s interest rate cuts could help ease some pressure on the housing market, its ability to address rising housing costs is limited, as these increases are driven by a lack of affordable supply and increasing development costs. In fact, tight monetary policy hurts housing supply because it increases the cost of AD&C financing. This can be seen on the graph below, as shelter costs continue to rise at an elevated pace despite Fed policy tightening. Additional housing supply is the primary solution to tame housing inflation.
Furthermore, the election result has put inflation back in the spotlight and added some downside risks to the economic outlook. Proposed tax cuts and tariffs could increase inflationary pressures, suggesting a more gradual easing cycle with a slightly higher terminal federal funds rate. Given the housing market’s sensitivity to interest rates, this could extend affordability crisis and constrain housing supply as builders continue to grapple with lingering supply chain challenges.
During the past twelve months, on a non-seasonally adjusted basis, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 2.7% in November, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ report. This followed a 2.6% year-over-year increase in October. Excluding the volatile food and energy components, the “core” CPI increased by 3.3% over the past twelve months, the same increase as in the previous two months. The component index of food rose by 2.4%, while the energy component index fell by 3.2%.
On a monthly basis, the CPI rose by 0.3% in November on a seasonally adjusted basis, after a 0.2% increase in October. The “core” CPI increased by 0.3% in November, the same increase as in the past three months.
The price index for a broad set of energy sources rose by 0.2% in November, with declines in electricity (-0.4%) offset by increases in gasoline (+0.6%), natural gas (+1.0%) and fuel oil (+0.6%). Meanwhile, the food index rose 0.4%, after a 0.2% increase in October. The index for food away from home increased by 0.3% and the index for food at home rose by 0.5%.
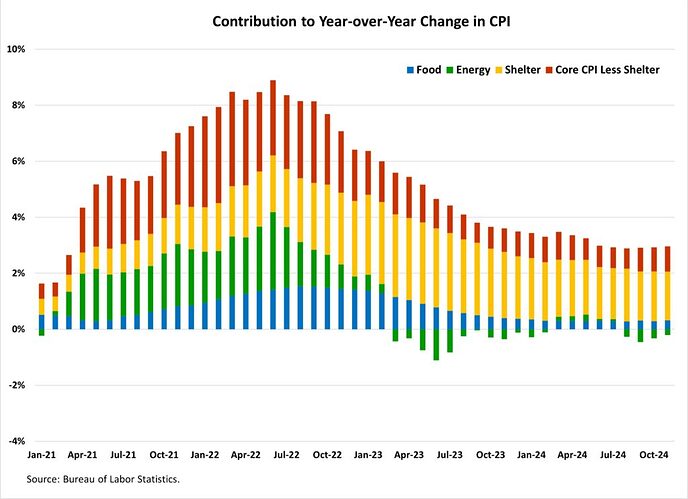
The index for shelter (+0.3%) was the largest contributor to the monthly increase in all items index, accounting for nearly 40% of the total increase. Other top contributors that rose in November include indexes for used cars and trucks (+2.0%), household furnishings and operations (+0.6%), medical care (+0.3%) and new vehicles (+0.6%). Meanwhile, the index for communication (-1.0%) was among the few major indexes that decreased over the month.
The index for shelter makes up more than 40% of the “core” CPI, rose by 0.3% in November after a 0.4% in October. Both indexes for owners’ equivalent rent (OER) and rent of primary residence (RPR) increased by 0.2% over the month. For the rent index, it was the smallest monthly increase since April 2021 and July 2021. Despite the moderation, shelter costs remained the largest contributors to headline inflation.
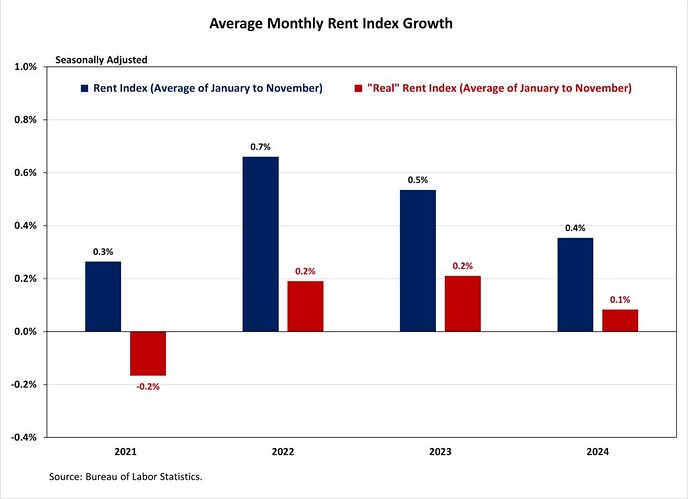
NAHB constructs a “real” rent index to indicate whether inflation in rents is faster or slower than overall inflation. It provides insight into the supply and demand conditions for rental housing. When inflation in rents is rising faster than overall inflation, the real rent index rises and vice versa. The real rent index is calculated by dividing the price index for rent by the core CPI (to exclude the volatile food and energy components).
In November, the Real Rent Index fell by 0.1%, marking its first negative reading since December 2021. Over the first eleven months of 2024, the monthly growth rate of the Real Rent Index averaged 0.1%, slower than the average of 0.2% in 2023.